Location:Home Page > Archive Archive
5 surge protection methods, how many do you know?
2023-10-03【Archive】
It is estimated that 75% of electronic device failures are due to transients and power surges. Transients and power surges are everywhere. Power grids, lightning strikes, explosions, and even people walking on carpets generate electrostatic induction voltages of tens of thousands of volts. These are invisible and deadly killers of electronic products.
Therefore, in order to improve reliability of electronic products and safety of human body itself, it is necessary to take measures to protect against power surges and power surges.

There are many causes of a burst, and a burst is a bursty pulse with a high slew rate and short duration.
Power surge, ignition switch, reverse supply, static electricity, motor/power supply noise, etc. are all factors that cause power surges. A surge protector provides a simple, economical and reliable method to protect electronic equipment from power surges.
As we all know, electronic products often encounter unexpected transients and power surges during use, resulting in damage to electronic products. The reason for damage is that semiconductor devices (including diodes, transistors, thyristors and integrated circuits, etc.) burn out or break.
One method is to ground entire machine and system. The ground (common end) of entire machine and system must be separated from ground. Each subsystem of entire machine and system must have an independent When data or signals are to be transferred between subsystems, ground must be used as a reference level, and ground wire (surface) must be capable of carrying a large current, such as hundreds of amperes.
The second method of protection is to use surge and surge protection devices in key parts of entire machine and system (such as computer monitors, etc.) so that transients and surges on subsystem can be bypassed. - Grounding and grounding of system, so that transient voltage and overvoltage amplitude applied to entire machine and system are greatly reduced.
The third protection method is to use a combination of several surge and surge protection devices for important and expensive complete machines and systems to form a multi-level protection scheme.
A surge protector is a simple, economical and reliable method of protecting electronic equipment from power surges. With surge protection element (MOV), it can quickly reduce lightning surges and surge operation. Energy is channeled into ground, protecting equipment from damage.
Surge Protection Methods
(1) Parallel line filter connected in parallel to power line
Under normal conditions, varistor in lightning protection module is in a high resistance state. When lightning strikes power grid or there is a momentary overvoltage during switching operations, lightning protection operates within nanoseconds and varistor is in a low resistance state, quickly limiting overvoltage to a very low amplitude.

When there is a long continuous pulse or a constant overvoltage in line, characteristics of varistor are degraded and heated to a certain extent, so that thermal shutdown mechanism is activated to prevent fire and protect equipment.
(2) Series filter surge protector connected in series with power line
Providing safe and clean power to valuable electronic equipment, lightning waves not only have tremendous energy, but also extremely high slew rates of voltage and current. Parallel arresters can only suppress amplitude of lightning waves, but cannot change their sharply rising front. An overvoltage protection device with a series filter is connected in series with power supply line.
In event of an overvoltage, MOV1 and MOV2 respond within nanometer time to limit overvoltage; at same time, LC filter reduces sudden rise in lightning wave voltage and current by almost 1000 times, and also reduces residual voltage by 5 times, thus protecting sensitive user equipment.
(3) Install voltage-sensitive arresters between phases and lines of power lines to limit voltage surges
The first method provides best protective effect for electrical equipment with high shock resistance, such as lighting, elevators, air conditioners and motors. But for modern electronic equipment with a high degree of integration and compact structure, actual protection effect is not satisfactory. The reasons are as follows:
Take inductive lightning protection of a 220V single-phase AC power supply as an example. A common method is to install a suitable pressure sensing element between neutral and ground wires to absorb and limit peak voltage generated by inductive lightning strike. The effect of lightning protection of a power line depends entirely on choice of parameters of varistor and reliability of the varistor.

Varistor limit selection is based on 310V mains peak power plus 20% mains fluctuation, 10% component dissipation errors, and 15% heat, humidity, and component aging caused by long-term operation. And compensation for other reliability factors, total value is 470V ~ 510V. Various peak interference voltages, such as induced lightning strikes, are limited to 470V. Below 470V, varistor does not work.
The power frequency withstand voltage of ordinary low-voltage electrical equipment (machinery, elevators, lighting, air conditioners, etc.) is usually 1500V AC, and peak instantaneous withstand voltage can reach more than 2500V, so 470V is very safe. However, operating voltage of modern electronic equipment composed of large-scale integrated circuits is usually ±5V to ±15V, and maximum withstand voltage value is usually not more than 50V, so high-frequency peak voltage of less than 470V superimposed on network will be directly routed. to input load, which is disproportionately transferred to switching power supply or integrated circuit chip through spatial coupling capacitance, interlayer and interelectrode capacitance of transformer, which can lead to failure.
Although high-frequency switching power supplies and electronic equipment have appropriate surge protection measures, protection effect is not ideal due to cost and volume limitations, combined with large variations in intensity and spectrum of peak interference such as conducted interference. lightning strikes. This is effect obtained with ideal position of varistor limiter. In fact, due to influence of residual voltage of varistor element and inductance of supply wire, when a strong induction lightning strikes, peak value of actual limit voltage may rise to 800-1000V or more, which threatens electronic equipment. after step.
(4) Improve protective effect of electronic equipment and connect an ultra-isolation transformer (also known as isolation method) in series between power supply and load to isolate high-frequency noise bursts, and in same time can facilitate secondary equipotential bonding.
The isolation method mainly uses an isolation transformer with a shielding layer. Since common mode noise is a type of ground noise, it is mainly transmitted through coupling capacitance between transformer windings. If shield layer is inserted between primary and secondary windings and is well grounded, noise voltage can be shunted through shield layer, thereby reducing noise voltage at the output.
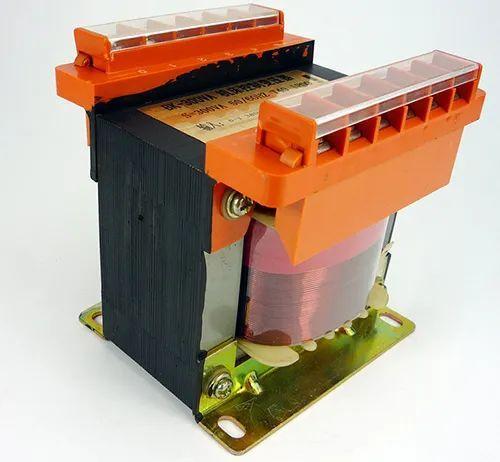

Theoretically, a transformer with a shielding layer can provide attenuation up to 60 dB. However, quality of insulation effect often depends on process of shielding layer. It is best to use a 0.2mm thick copper plate and add a shielding layer on primary and secondary sides. Usually, primary side protective layer is connected to secondary side protective layer through a capacitor, and then connected to secondary side ground. The primary side shield layer can also be connected to primary side ground wire, and secondary side shield layer can be connected to side ground wire. And cross-sectional area of the ground electrode must be larger. This is a good way to use an isolation transformer with a shielding layer, but it is larger.
Due to sole function of transformer, this method is relatively large in size and weight, not very convenient to install, and effect of protecting against medium and low frequency peaks and surges is not very good. Therefore, market is limited, and there are not many manufacturers. Therefore, it is usually not used in non-special cases.
(5) Absorption method
The absorption method mainly uses wave absorbing devices to absorb impulse peak noise voltage. All absorbing devices have a common feature, i.e. they have a high impedance below threshold voltage, and when threshold voltage is exceeded, impedance drops sharply, so it has a certain inhibitory effect on peak voltage.
This type of absorbing device mainly includes varistors, gas discharge tubes, TVS tubes, solid state discharge tubes, etc. Various absorbing devices also have their own peak voltage suppression limitations. For example, current absorption capacity of varistor is not large enough, and response speed of gas booster tube is relatively slow.
Related
- 5 surge protection methods, how many do you know?
- "Jingzhen" stroked you: "Do you know how I work?"
- Count 8 most commonly used diodes! How much do you know?
- How to choose a suitable power chip, do you know this?
- Four Magic DMM Methods You Should Know
- Circuit Analysis of 6 Examples Explaining Lightning Surge Protection in Detail
- What do you know about fuse classification?
- Do you know 4 characteristics of Schottky diodes?
- RC downgrade secret, I don't know how many people will be fooled
- Do you know everything about communication, decoupling and capacitance?
Hot Posts
 How to distinguish induction from leakage, we will teach you three tricks! Ordinary people can also learn super practical
How to distinguish induction from leakage, we will teach you three tricks! Ordinary people can also learn super practical
- What is drowning in gold? Why Shen Jin?
- This is a metaphor for EMI/EMS/EMC that can be understood at a glance.
- How many types of pads have you seen in PCB design?
- Summary of Common PCB Repair Techniques
- What is three anti-paint? How to use it correctly?
- Knowing these rules, you will not get confused looking at circuit diagram.
- How to make anti-interference PCB design?
- Can diodes do this?