Location:Home Page > Archive Archive
Why do diodes conduct electricity in one direction? understand in seconds
2023-03-19【Archive】
A diode is a very commonly used component in electronic circuits. It has characteristics of forward conduction and reverse cutoff.
Apply a positive voltage to positive terminal (positive pole) of diode and a negative voltage to negative terminal (negative pole), diode will conduct and current will flow through it.
A negative voltage is applied to positive end (positive pole) of diode, and a positive voltage is applied to negative end (negative pole). The diode turns off and no current flows through it.
This is unidirectional conduction characteristic of so-called diode.
The following explains why a diode conducts current in one direction.
Unidirectional diode conduction
A diode is composed of a PN junction, that is, a P-type semiconductor and an N-type semiconductor, so characteristics of PN junction result in unidirectional conduction of diode. The PN junction is shown in Figure 1.
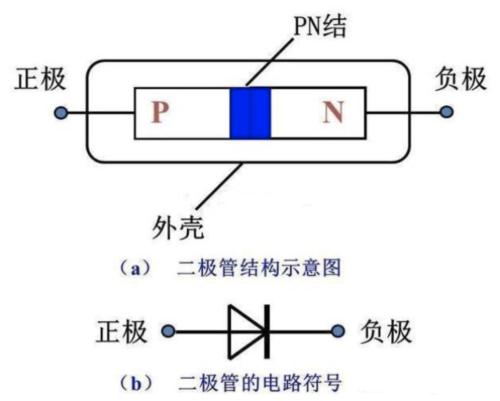
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of a PN connection
Near boundary between P-type and N-type semiconductors, due to large concentration of free electrons in N-region, negatively charged free electrons will diffuse from N-region to P-region with a low electron concentration; As a result of diffusion, a PN junction is formed. The side near P region is negatively charged, and side near N region is positively charged, forming an electric field from N region to P region, that is, an electric field inside PN node. The internal electric field will prevent continued diffusion of majority carriers, also known as blocking layer.
Detail node PN
One-sided conduction of diodes is very useful. What makes electrons so obedient? What is its microscopic mechanism? Here is a brief introduction.
Suppose there is a P-type semiconductor (yellow represents more holes) and an N-type semiconductor (green represents more electrons). Both of them are electrically neutral in their natural state, that is, they are not charged. as shown in Figure 2.
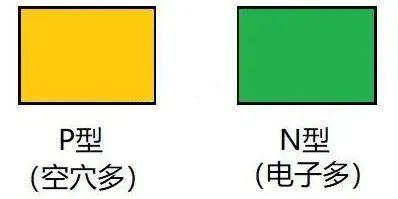
Fig. 2. P-type and N-type semiconductors
Connect them together to form a PN connection. The electrons in an N-type semiconductor at boundary will naturally move into P-type region to fill holes, leaving atoms that lose electrons and become positively charged.
Atoms at boundary of corresponding P-type region are negatively charged due to addition of electrons, so a space charge region is formed at boundary.
Why is it called "space charge region"? Because these charges are made up of atoms that cannot move in microscopic space.
The space charge region forms a built-in electric field, and direction of electric field is from N to P. This electric field prevents subsequent electrons from continuing to fill holes, because negative space charge in P region repels electrons at this time.
The combination of electrons and holes will get slower and slower and finally reach a balance that is equivalent to carrier depletion, which is why space charge region is also called a depletion layer.
At this time, PN junction is still electrically neutral overall because positive and negative space charges cancel each other out. As shown in Figure 3.
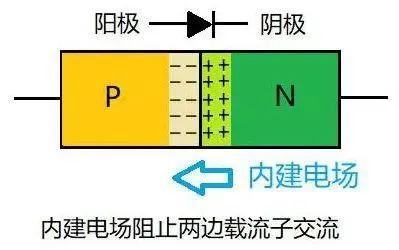
Fig. 3. PN junction forms a built-in electric field
An external forward voltage is applied, and direction of electric field changes from positive to negative, which is opposite to built-in electric field and weakens built-in electric field, so diode conducts easily.
Green arrows indicate direction of electron flow, opposite to direction determined by current flow. As shown in Figure 4.
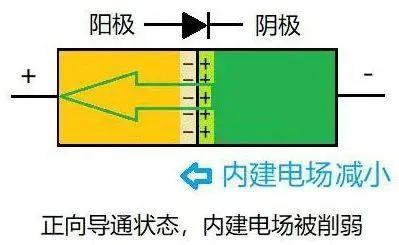
Fig. 4. State of direct conduction
When reverse voltage is applied, direction of electric field is same as that of built-in electric field, which strengthens built-in electric field, so diode is not easy to conduct. As shown in Figure 5.
Of course, non-conductivity is not absolute, there will usually be a small amount of leakage current. If reverse voltage continues to increase, it can cause diode to break down and drain quickly.
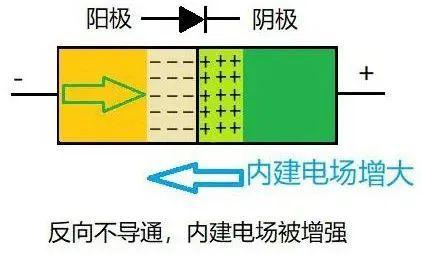
Fig. 5. Reverse state of no conduction
In fig. 6 shows current-voltage characteristic of diode for reference.
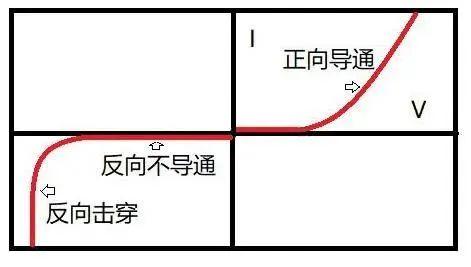
Fig. 6. Diode voltage and current curve
Figure 7 clearly shows why diodes in different directions may or may not conduct, which is easy to understand.
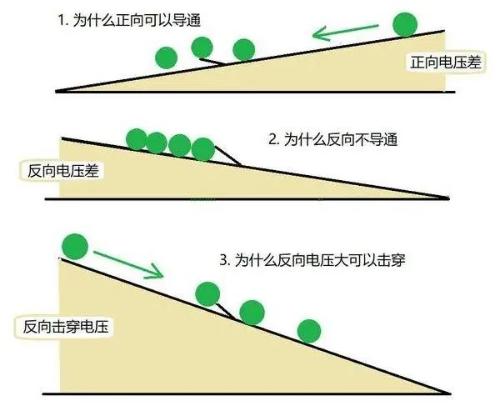
Fig. 7. Different conduction effects in different directions
There are many examples of one-way conduction in life. For example, a one-way gate at entrance to a subway station is also equivalent to diode effect: forward conduction, reverse non-conductivity If you insist on passing in opposite direction, gate may be damaged due to too much "backward breakdown" .
Related
- Why do diodes conduct electricity in one direction? understand in seconds
- Understand in seconds! How gyroscopes work
- Understand Current Detection Circuit in One Article
- Do you understand MOS driver in motor controller?
- Ever thought that diodes could still be used in this way?
- Can diodes do this?
- What is drowning in gold? Why Shen Jin?
- Why is there no current limiting resistor in LED?
- Why is electricity divided into AC and DC?
- Why are there always two capacitors in circuit 0.1uF and 0.01uF?
Hot Posts
 How to distinguish induction from leakage, we will teach you three tricks! Ordinary people can also learn super practical
How to distinguish induction from leakage, we will teach you three tricks! Ordinary people can also learn super practical
- What is drowning in gold? Why Shen Jin?
- This is a metaphor for EMI/EMS/EMC that can be understood at a glance.
- How many types of pads have you seen in PCB design?
- Summary of Common PCB Repair Techniques
- What is three anti-paint? How to use it correctly?
- Knowing these rules, you will not get confused looking at circuit diagram.
- How to make anti-interference PCB design?
- Can diodes do this?