Location:Home Page > Archive Archive
What is a magnetic sensor? The most common types of magnetic sensors and their applications
2023-03-18【Archive】
01 What is a magnetic sensor?
A magnetic sensor is usually understood as transformation of magnitude and change of magnetic field into an electrical signal.
The magnetic field, represented by Earth's magnetic field (geomagnetism) or magnet, is a familiar but invisible phenomenon. Magnetic sensors that convert invisible magnetic fields into electrical signals and visible effects have long been subject of research.
From decades ago, sensors using electromagnetic induction effect, to modern applications using magnetoelectric effect, magnetoresistance effect, Josephson effect and other physical phenomena.

02 A typical magnetic sensor and its application
Sensors using various physical effects are now commercially available. Below we will focus on most commonly used types of magnetic sensors and their applications.
【MR Sensor Element】
The MR sensor element is a magnetic sensing element that uses effect of magnetoresistance (MR effect). There are many types of MR sensors that use different principles of operation.
The MR effect is a phenomenon in which resistance changes depending on magnetic field. This effect occurs in magnetic materials such as iron, nickel or cobalt.
Understanding MR effect requires an understanding of electron's spin and how Lorentz force works on electron's charge.
When electrons move in ferromagnetic materials (materials with certain magnetic properties), spin of electrons fluctuates and probability of scattering (electrons) in magnetic materials will increase or decrease. This is what causes MR effect.
An electron has two important parameters: charge and spin. They have same negative charge, but electrons have two kinds of spin: up and down. In 1922, spin of electron was tested experimentally, and it was confirmed that electron has characteristics of angular momentum and magnetic moment of electron.
When electrons pass through conductive materials, they are scattered (electron scattering). Electron scattering is a phenomenon in which static electricity in a material causes electrons to deviate from their normal path.
The Lorentz force is force exerted when moving charged particles (electrons) in a conductive material are subjected to a magnetic field. It affects all charged particles and does not depend on electron spin.
【AMR sensor element】
In 1856, William Thomson discovered anisotropic magnetoresistance effect (AMR effect) by observing ferromagnetic materials placed in an external magnetic field.
When direction of magnetization of a ferromagnetic material is parallel to current flow, electron orbits are perpendicular to current flow, resulting in maximum resistance. This increases spin-dependent scattering, resulting in an increase in resistance.
When direction of magnetization is perpendicular to current flow, orbits of electrons are parallel to current flow, which reduces spin dependent scattering and creates minimal resistance.
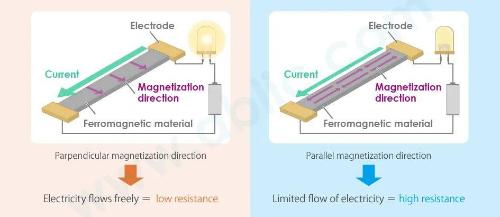
The rate of change in resistance caused by state of magnetic field is called magnetoresistance coefficient (MR coefficient). The MR ratio of AMR sensor element is about 5%. AMR touch elements are commonly used in magnetic switches and rotary encoders due to their simple design.
【TMR Sensor Element】
The tunneling magnetoresistance effect (TMR effect) at room temperature was discovered in 1995 by Professor Terunobu Miyazaki of Tohoku University in Japan. The TMR sensing element is a magnetic sensing element that uses TMR effect and consists of an extremely thin nanoscale non-magnetic insulating layer sandwiched between two ferromagnetic layers. The electrons tunnel from one ferromagnetic layer to another through insulating layer. This is a quantum mechanical phenomenon.
When directions of magnetization of two ferromagnetic materials are parallel, resistance decreases, and when they are not parallel, resistance increases.
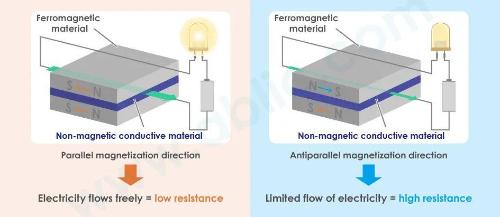
The MR coefficient (rate of change of resistance depending on state of magnetic field) at TMR junction can reach more than 100% in production. Under laboratory conditions, it reached levels of over 1000%.
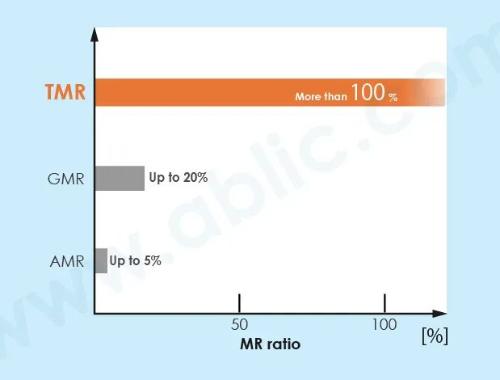
Because of their high sensitivity, TMR sensor elements are ideal for hard drive heads or highly sensitive rotation angle sensors.
【Hall Element】
The Hall element is an application of Hall effect. The Hall effect, discovered by Edwin H. Hall in 1879, demonstrated that Lorentz force produces a voltage at right angles to direction of current and magnetic field. This voltage is called Hall voltage, and according to Fleming's left hand rule, direction of voltage changes with direction of magnetic flux. The magnitude and direction (positive, negative) of voltage make it possible to determine magnitude and direction of magnetic field (pole N, pole S).
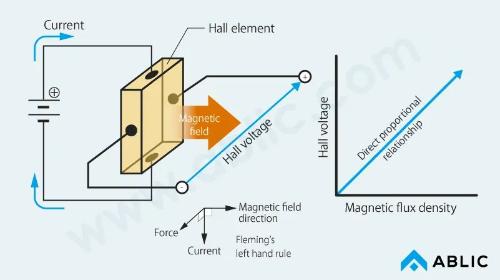
Hall elements are less sensitive to magnetic fields than magnetoresistive sensor elements. However, as a magnetic sensor that does not rely on magnetic materials, it can be used in ferromagnetic fields or harsh environments, so it can be used as a current sensor or various magnetic switches.
03 ABLIC magnetic sensor
ABLIC now offers Hall sensor and TMR sensor ICs consisting of silicon Hall elements and signal processing circuits, as well as signal processing circuits.
We can provide perfect product for your application and environmental requirements.
ABLIC is committed to creating a safe and livable society by offering and providing magnetic sensor solutions with our technology, taking advantage of our sensor elements.
Related
- What is a magnetic sensor? The most common types of magnetic sensors and their applications
- What is difference between 0 ohm resistors, inductors and magnetic balls? After reading this I finally got the answer
- What is difference between 0 ohm resistors, inductors and magnetic balls for single point grounding?
- What does color of magnetic ring mean?
- Do not underestimate "form of high-frequency magnetic core" in switching power supply, what effect does it have on transformer?
- What is purpose of connecting a polar capacitor and a non-polar capacitor in parallel?
- What is power supply ripple, how to measure their magnitude and how to suppress?
- A list of most common PCB design mistakes, see how many mistakes have you made?
- What is a delay scheme? Explanation of 6 Kinds of Delay Circuit Principles
- Four ways to reduce the output "ripple and noise" of a switching power supply
Hot Posts
 How to distinguish induction from leakage, we will teach you three tricks! Ordinary people can also learn super practical
How to distinguish induction from leakage, we will teach you three tricks! Ordinary people can also learn super practical
- What is drowning in gold? Why Shen Jin?
- This is a metaphor for EMI/EMS/EMC that can be understood at a glance.
- How many types of pads have you seen in PCB design?
- Summary of Common PCB Repair Techniques
- What is three anti-paint? How to use it correctly?
- Knowing these rules, you will not get confused looking at circuit diagram.
- How to make anti-interference PCB design?
- Can diodes do this?