Location:Home Page > Archive Archive
What is difference between synchronous rectification and non-synchronous rectification?
2023-03-18【Archive】
The switching power supply is designed to charge inductor when power tube is turned on, and inductor accumulates energy; when power tube is turned off, inductor releases energy, thereby realizing voltage conversion.

When power tube is off, inductor needs a current loop to release power. Different selection of freewheel components will include different rectification methods, namely synchronous rectification and asynchronous rectification.
What is difference between synchronous rectification and non-synchronous rectification?
One difference between synchronous and asynchronous
01 Asynchronous
Take a BUCK circuit as an example, if there is only one MOS lamp (power lamp) in circuit, and a rectifier diode is used in freewheel circuit (the diode is unidirectional, no external control circuit is required). its on-off), then circuit is asynchronous because it has only one mos lamp (or switch lamp) to drive circuit, and flyback diode does not need a control circuit, so there is no need to emphasize synchronous driving diode (D1) , which can be understood as a synchronous non-synchronous, non-synchronous circuit shown in Figure 1.
Picture 1
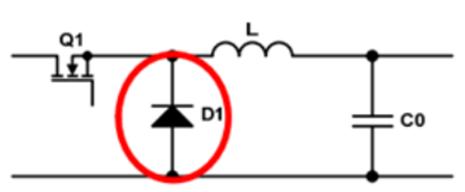
02 Synchronization
If MOS tube (Q2) is also used in freewheel circuit in chain, then top and bottom tubes are MOS tubes, since MOS tube itself is a component that requires external control. The rectification process must be based on power supply. The switching sequence drives Q1 and Q2 synchronously, so circuit is synchronous, and the synchronous circuit is shown in fig. 2:
Picture 2
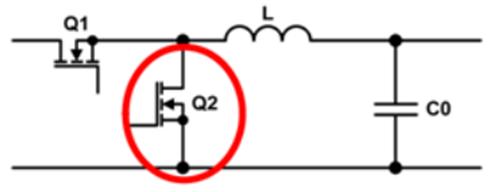
Synchronization is a new technology that uses high power MOSFETs with extremely low on-resistance instead of rectifier diodes to reduce rectification losses; it can greatly improve efficiency of DC/DC converters.
The high power MOS lamp is a voltage controlled device and its current-voltage characteristics are linear when it is turned on. When a power MOS lamp is used as a rectifier, gate voltage must be synchronized with phase of rectified voltage in order to complete rectification function, so it is called synchronous rectification.
Two advantages and disadvantages of synchronous and asynchronous
01 Advantages and disadvantages of asynchronous mode
High stability
Because Schottky diode is passive, synchronous device circuit will not conduct both top and bottom transistors at same time, so its stability is higher than that of synchronous arrangement circuit.
Low efficiency
When current flowing through Schottky diode is large, voltage generated by free current across diode is relatively large (about 0.5V), and when output voltage is very low, voltage drop across diode is a large part. relatively large power, so efficiency is low at high current and low output voltage.
02 Synchronization advantages and disadvantages
Higher efficiency
The internal resistance of a conventional MOS lamp is very low. With same current flowing, conduction voltage drop across it is much smaller than forward conduction voltage drop of a conventional Schottky diode, and power loss of a MOS tube is much higher than that of a diode. It is small, so efficiency of synchronous rectification will be higher.

Insufficient stability
Mos tube needs a drive circuit, while synchronous rectification needs to add an additional control circuit for MOS tube so that upper and lower MOS tubes can be synchronized. Compared to asynchronous, synchronous control scheme is relatively complex. more complex circuit, less stable it is. Reliably, if you mix up logic and turn on upper and lower lamps at same time, system will definitely fail.
Three synchronous and non-synchronous options
The choice between synchronous or asynchronous mode is mainly considered based on three aspects: efficiency, cost and reliability.
For higher output voltage and higher duty cycle, power consumption of Schottky diode in asynchronous system and low power synchronous rectifier tube is relatively small. At this time, conversion efficiency of synchronous rectification and non-synchronous rectification difference is not obvious.
For applications with low output voltage, low duty cycle, and high current, conversion efficiency of synchronous rectification is relatively high.
Summarizing, if requirements for high efficiency are relatively high, and requirements for cost and reliability are not too high, then you can choose a synchronous rectification scheme; if efficiency requirements are not very high, asynchronous rectification is preferable and its reliability is higher.
Related
- What is difference between synchronous rectification and non-synchronous rectification?
- What is difference between TVS tube and zener diode?
- What is difference between thermocouple and RTD? Remember these points, do not choose wrong
- What is difference between 0 ohm resistors, inductors and magnetic balls for single point grounding?
- What is difference between surge device, lightning arrester, leakage protection, circuit breaker and circuit breaker? Come and get knowledge
- What is difference between 0 ohm resistors, inductors and magnetic balls? After reading this I finally got the answer
- What is difference between stepper/brush/brushless motors? remember this list
- What is purpose of connecting a polar capacitor and a non-polar capacitor in parallel?
- You will understand difference between input impedance and output impedance after reading this article!
- You will understand difference between input impedance and output impedance by reading this article.
Hot Posts
 How to distinguish induction from leakage, we will teach you three tricks! Ordinary people can also learn super practical
How to distinguish induction from leakage, we will teach you three tricks! Ordinary people can also learn super practical
- What is drowning in gold? Why Shen Jin?
- This is a metaphor for EMI/EMS/EMC that can be understood at a glance.
- How many types of pads have you seen in PCB design?
- Summary of Common PCB Repair Techniques
- What is three anti-paint? How to use it correctly?
- Knowing these rules, you will not get confused looking at circuit diagram.
- How to make anti-interference PCB design?
- Can diodes do this?