Location:Home Page > Archive Archive
What is difference between thermocouple and RTD? Remember these points, do not choose wrong
2023-04-16【Archive】
In our daily work, we often come across devices for measuring temperature. Thermistor and thermocouple are instruments for measuring temperature. What to choose: RTD or thermocouple for same temperature measurement point? Today we will analyze it completely.
01 Thermocouple structure
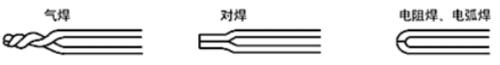
There are 3 types of thermocouple tip connection shape, as shown in figure below. Depending on type of thermocouple, wire diameter and operating temperature, it can be connected by gas welding, butt welding, resistance welding, arc welding, silver welding, etc.
In industrial applications, an outer sheath is commonly used to facilitate mounting and extend the life of thermocouples. The body is generally divided into protective tube type and armored type.
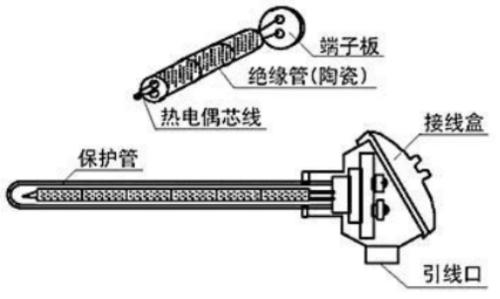
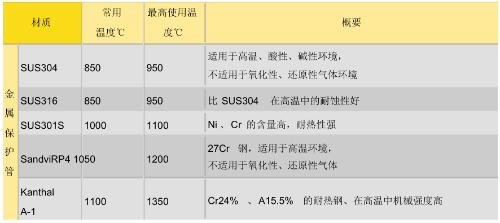
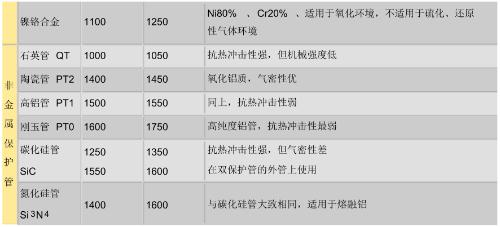
The thermocouple with protective tube is a thermocouple in which thermocouple core and insulating tube are inserted into protective tube. By protecting core from oxidation and corrosion, protective tube can also maintain mechanical strength of thermocouple. There are many types of protective tubes, most commonly used are shown in table below.
02 Armored thermocouple
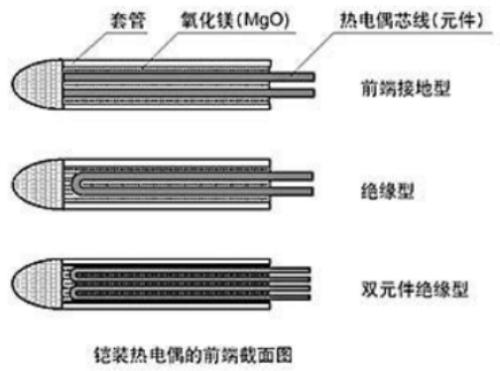
The measurement principle of an armored thermocouple is same as that of a thermocouple with a protective tube. It uses a thin metal tube (called a sleeve) instead of insulating tube (ceramic) pictured above, and uses a powder such as magnesium oxide (MgO) as insulating material.
With its thin outer diameter and slight curve, it is best suited for measuring temperature of back of an object and narrow gaps. In addition, its response speed is more sensitive than thermocouple with protective tube.
Sheathed thermocouple has a wide range of outside diameters and can be extended and machined to various sizes from 8.0 mmph to 0.5 mmph. The thinner strand is stretched, lower upper limit of commonly used temperature.
For example, for a K-type thermocouple, general upper temperature limit for a 0.5mm OD case is 600°C, and for a 8.0mm OD, it is 1050°C.
Thermal resistance structure
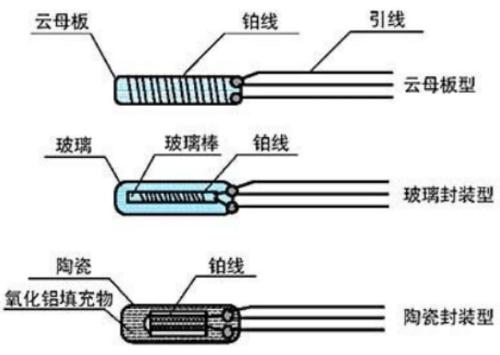
As shown in figure below, there are three types of heat-resistant element shapes, and ceramic case type is currently predominant. The ceramic coated version is used for RTDs with protective tubes and armored RTDs.
Platinum wires with ceramic and glass packages have a diameter of about tens of microns, and mica plates have a diameter of about 0.05 mm. The lead wires use platinum alloy wires, which are much thicker than component wires.
03 Types of heat-resistant elements
Temperature resistance example with protective tube
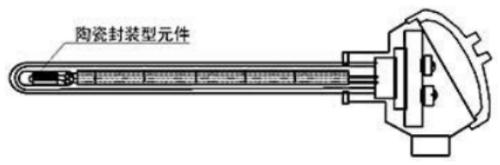 Armored thermal resistance
Armored thermal resistance
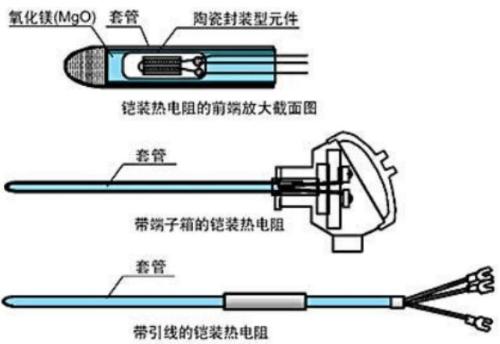
04 Difference
1. Although they are all contact temperature measuring instruments, their temperature measuring ranges are different. Thermocouples are used in higher temperature environments, since their output thermoelectric potential is very low in range of medium and low temperatures (see table). are very high, otherwise measurement will not be possible. In addition, in lower temperature region, relative error caused by change in temperature of cold junction and change in ambient temperature is very noticeable, and it is not easy to fully compensate for it.
At present, when temperature is low and medium, thermal resistance is generally used to measure temperature in range of 200-500, and even lower temperature can be measured (for example, a low temperature of about 1K can be measured). measured using carbon resistance).Now thermal resistance of platinum is commonly used Resistor Pt100, (there are also Pt50, 100 and 50 representing resistance value of thermal resistance at 0 degrees, which are represented by BA1 and BA2 in old graduation, and resistance value of BA1 is 46 ohms at 0 degrees, which is also useful in industry.Copper resistors, CU50 and CU100 graduations, but temperature measurement range is small, from 50 to 150, in some special cases.there are indium resistors, manganese resistors, etc.)
2.The main principle of thermocouple temperature measurement is thermoelectric effect, and secondary meter is a voltmeter or electronic potentiometer to improve accuracy. Resistors work based on characteristic that resistance value of conductors and semiconductors varies with temperature, and secondary meter is an unbalanced bridge.
3.According to principle of thermocouple temperature measurement, only when temperature of cold end is constant, measured temperature has an unambiguous functional relationship with thermoelectric potential.In actual use, thermoelectric characteristic and corresponding low-cost connection wires (also called compensating wires) with similar characteristics are used , extending cold end of thermocouple to a location with a relatively constant temperature (preferably 0 degrees), for example, using a copper-constantan compensating wire to extend nickel-chromium--nickel-silicon thermal resistance. Therefore, there are two extension wires from thermocouple to secondary meter.
Thermal resistance and secondary meter are connected by copper wires. In order to reduce measurement error caused by environmental changes, three-wire connection method is usually used. There are two wires connecting thermal resistance in series with two adjacent wires. On first leg of bridge, other wire must carry power. When using itThe implementation requires that sum of resistance value of each wire and control resistance is guaranteed to be 5 ohms (±0.01) .
05 On-site assessment in progress
1. Thermocouple. Thermocouples have positive and negative poles, and compensating wires also have positive and negative poles. First of all make sure connection is correct and configuration is correct. In operation, short circuits, open circuits, poor contact (can be judged with a multimeter) and wear (revealed by color of surface) are common. When checking, thermocouple should be separated from secondary meter.
The method I evaluate in practice is for reference: use tool to short compensation line on secondary meter, meter shows room temperature (if not, meter is faulty), then short thermocouple terminal, meter shows thermocouple Ambient temperature, where it is located (no, compensation line is faulty), and then using mv file of multimeter, roughly estimate thermoelectric potential of thermocouple (if it is normal, check process).
2. Thermal resistance: This is nothing more than a short circuit and an open circuit, which can be judged with a multimeter. During operation, if you suspect a short circuit, simply disconnect end of wire from end of resistance and look at indicator, if it reaches maximum value, thermal resistance is shorted, returns to zero, or wire is shorted. -closed Make sure connection and configuration are correct If meter reading is low or unstable, protect The pipe may be flooded.
Maximum display, open circuit thermal resistance, minimum display, short circuit. Generally speaking, thermal resistance is used for temperatures below 300 degrees and thermocouples are used for temperatures above 300 degrees. When temperature changes, resistance of thermistor will change, and thermoelectric potential of thermocouple will change.
Currently, thermal resistances are copper thermal resistances and platinum thermal resistances, which are divided into different graduations according to thermal resistance value at 0 degrees, such as PT100, PT1000, CU50, etc., taking as an example PT100. , PT means platinum, 100 means thermal resistance resistance value at 0 degrees is 100 ohms.
Today, thermocouples usually have serial numbers such as K, B, and S, which represent different materials and are used in different temperature ranges. For example: K type is nickel-chromium-nickel-silicon material, usually measuring 0-800 degrees, type B is platinum-rhodium 30-platinum-rhodium 6, usually measuring 800-1600 degrees.
06 What is principle of thermocouple measurement?
The principle of operation of a thermocouple is based on Seebeck effect (Seebeck effect), that is, two conductors with different components are connected in a loop. If temperature of two ends of connection is different, physical phenomenon of thermal current will occur. generated in a loop. A thermocouple consists of two different wires (thermods) welded together at one end to form measuring end (also called working end) of thermocouple.
Place it in an environment with a measured temperature, and connect other end of thermocouple (conditional junction or free end) to an indicator device. If there is a temperature difference between measuring end of thermocouple and reference end, instrument will display thermoelectromotive force generated by thermocouple.
07 What is principle of measuring thermal resistance?
Thermal resistance measures temperature using characteristics that resistance of a metal conductor or semiconductor changes with temperature change. wires formed on a frame or formed on a substrate in a laser deposition process.
When measured medium has a temperature gradient, measured temperature is average temperature of layer of medium within range in which temperature sensitive element is located.
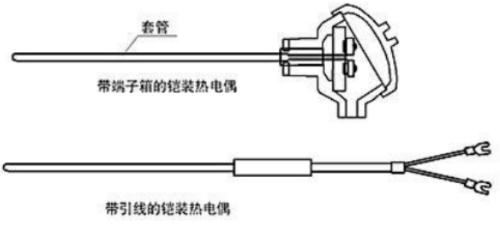
08 What is an armored thermocouple and what are its advantages?
In IEC1515 standard, term "Mineral Insulated Thermocouple Cable" refers to an inorganic mineral insulated thermocouple cable. The thermoelectrode, insulator and sheath are made by whole drawing method, and outer surface is, as it were, covered with a layer of “armor”, therefore thermocouple is called armored.
Compared with conventional thermocouple assembly, it has advantages of high pressure resistance, good flexibility, good oxidation resistance and long service life.
09 What are serial numbers of thermocouples? What are specifications?
Thermocouple numbers mainly include S, R, B, N, K, E, J, T and so on. Among them, S, R, and B refer to noble metal thermocouples, and N, K, E, J, and T refer to base metal thermocouples.
Graph S is characterized by high oxidation resistance, suitable for continuous use in oxidizing and inert environments, long-term use temperature is 1400°C, short-term use temperature is 1600°C. Of all thermocouples, S graduation has highest accuracy class and is commonly used as standard thermocouples.
Compared with S scale, thermoelectric force of R scale is about 15% larger, and other characteristics are almost same.
The thermal electromotive force of graduation B is extremely lowat room temperature, so it is usually not necessary to use a compensating wire during measurement. Its long-term use temperature is 1600°C, and its short-term use temperature is 1800°C. It can be used in an oxidizing or neutral atmosphere, and can also be used briefly under vacuum conditions.
The N gradient is characterized by strong high-temperature oxidation resistance at 1300°C, long-term stability of thermoelectromotive force and good reproducibility of short-term thermal cycle, good nuclear radiation resistance and low temperature resistance, and can partially replace S thermocouple graduation.
K calibration marks are characterized by high resistance to oxidation and are suitable for continuous use in oxidizing and inert environments. The long-term use temperature is 1000°C and short-term use temperature is 1200°C. The most widely used of all thermocouples.
The characteristic of calibration number E is that among widely used thermocouples, its thermoelectromotive force is largest, that is, sensitivity is highest. It is suitable for continuous use in oxidizing and inert atmosphere, and operating temperature is 0-800°C.
The characteristic of J graduation is that it can be used in both oxidizing atmospheres (upper operating temperature limit 750°C) and reducing atmospheres (upper operating temperature limit 950°C). C), it is resistant to corrosion by H2 and CO gases. It is mainly used in oil refining and chemical industries.
The T-scaling has highest accuracy class of any base metal thermocouple and is typically used to measure temperatures below 300°C.
10 What is difference between N-type thermocouples and K-type thermocouples? What are pros and cons?
N-Type Thermocouple Benefits:
-High resistance to oxidation at high temperatures and long-term stability. Preferential oxidation of Cr and Si elements in positive electrode of nickel and chromium of K-type thermocouple causes uneven alloy composition, thermo-electromotive force drift, etc., and also increases content of Cr and Si in N-type thermocouples.
Change oxidation mode of nickel-chromium alloy from internal oxidation to external oxidation so that oxidation reaction only occurs on surface.
-Good stability during short-term thermal cycle at low temperature and suppressed magnetic transition;
-Strong ability to resist nuclear radiation, N-type thermocouple neutralizes perishable elements Mn and Co in K-type thermocouple, further enhancing ability to resist neutron radiation;
-In range of 400~1300℃, thermoelectric linearity of N-type thermocouple is better than that of K-type thermocouple.
Disadvantages of N-type thermocouples:
-N-type thermocouple material is harder than K-type, and more difficult to process;
- The price is relatively expensive. The thermal expansion coefficient of N-type thermocouple is 15% lower than that of stainless steel, so outer body of N-type armored thermocouple should be made of NiCrSi/NiSi alloy, non-linearity error is large in range of -200~400°C.
11 How many heat resistance output methods are there? What are effects?
There are 3 ways to output thermal resistance: 2-wire system, 3-wire system, and 4-wire system.
Connecting a 2-wire thermal resistor is simple, but it will introduce additional lead resistance error. Therefore, it is not suitable for making level A precision thermistors, and lead wires and wires should not be too long when used.
The three-wire system can eliminate effect of lead resistance, and measurement accuracy is higher than that of two-wire system. As a process discovery element, it is most widely used.
The 4-wire system can not only eliminate effect of wire resistance, but also eliminate effect of this resistance when connection wires have same resistance. When measuring with high accuracy, a 4-wire system should be used.
12 How to choose a thermocouple and thermal resistance?
Selection according to temperature measurement range. Typically, thermocouples are selected for temperatures above 500 °C and thermistors for temperatures below 500 °C.
Select according to measurement accuracy: select thermal resistance for high accuracy requirements and select thermocouple for low accuracy requirements.
Choose according to measurement range. Thermocouples typically refer to "spot" temperatures, and thermistors to average room temperatures.
Related
- What is difference between thermocouple and RTD? Remember these points, do not choose wrong
- What is difference between stepper/brush/brushless motors? remember this list
- What is difference between TVS tube and zener diode?
- What is difference between synchronous rectification and non-synchronous rectification?
- What is difference between 0 ohm resistors, inductors and magnetic balls for single point grounding?
- What is difference between surge device, lightning arrester, leakage protection, circuit breaker and circuit breaker? Come and get knowledge
- What is difference between 0 ohm resistors, inductors and magnetic balls? After reading this I finally got the answer
- step-down capacitor pay attention to these six points, do not need to worry about circuit analysis
- Please remember these 4 points to switch power supply in order to "comply with safety regulations".
- You will understand difference between input impedance and output impedance after reading this article!
Hot Posts
 How to distinguish induction from leakage, we will teach you three tricks! Ordinary people can also learn super practical
How to distinguish induction from leakage, we will teach you three tricks! Ordinary people can also learn super practical
- What is drowning in gold? Why Shen Jin?
- This is a metaphor for EMI/EMS/EMC that can be understood at a glance.
- How many types of pads have you seen in PCB design?
- Summary of Common PCB Repair Techniques
- What is three anti-paint? How to use it correctly?
- Knowing these rules, you will not get confused looking at circuit diagram.
- How to make anti-interference PCB design?
- Can diodes do this?