Location:Home Page > Archive Archive
What is difference between surge device, lightning arrester, leakage protection, circuit breaker and circuit breaker? Come and get knowledge
2023-03-18【Archive】
Now every household is inseparable from use of electricity, and safety of household appliances is becoming increasingly important for everyone. In order to protect our electrical safety, all kinds of devices have been produced that can disconnect circuit. Among them, surge protection devices, lightning arresters, leakage protection, circuit breakers, circuit breakers are more familiar to everyone. t tell them apart. What are differences between these types of protection devices? Today we will learn about differences between surge protection devices, surge arresters, leakage protection, circuit breakers and circuit breakers. Hope I can help everyone.
The difference between a spike and an open circuit
1) Line filter
A surge protection device (SPD), also known as a "lightning conductor" and "lightning conductor", is designed to limit overvoltage caused by severe transient overvoltage in electrical circuits and communication lines in order to protect equipment.
The principle of its operation is that in event of an instantaneous overvoltage or overcurrent in line, overvoltage protection device is quickly activated, and overvoltage in line is discharged to ground.

According to different protection equipment, it can be divided into two types: surge protection device and surge protection device.
The surge protector can be divided into primary surge protector, secondary surge protector, tertiary surge protector and quadruple surge protector according to same capacity;
Surge protection devices for signals can be divided into surge protection devices for network signals, surge protection devices for video signals, three-in-one surge protection devices for monitoring, surge protection devices for control signals, surge protection devices for overvoltages for antenna feeders, etc.
2) Air switch
An air circuit breaker is also called a circuit breaker. When current in circuit exceeds rated current, it will automatically turn off and protect circuit or electrical equipment from short circuit and overload.
For example, lighting, pumping and other energy sources can be controlled using air switches.

Its working principle is that when current passing through switch exceeds a certain current, metal sheet will bend due to heat, switch will operate and power will be turned off to protect equipment in line from being damaged by excessive current.
3) The difference between them
Works differently:
When momentary overvoltage in line increases, surge protection device will turn on in time to discharge overvoltage in line to ground; and air circuit breaker will automatically open when line current exceeds rated current. Take care of electrical equipment.
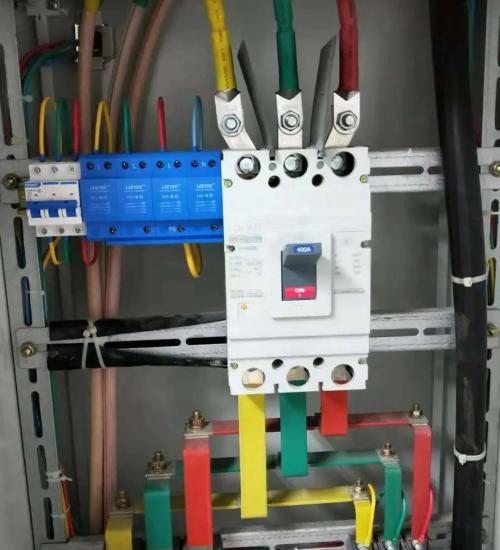

The protective effect is different:
A surge protector is a device to protect electrical and communication equipment in a line from being damaged by overvoltage in a line, and an air circuit breaker is designed to protect against short circuit and overload in a line.
The amount of protection is different:
The surge protector can not only protect power supply, but also protect communication line equipment, air circuit breaker protects electrical equipment.
Difference between air circuit breaker, leakage protection and circuit breaker
In a broad sense, an air circuit breaker refers to all circuit breakers using air as medium for isolating and extinguishing arc. Including air circuit breakers, air load breakers, air isolating circuit breakers, etc.
In this sense, low voltage box circuit breakers, molded case circuit breakers, miniature circuit breakers, circuit breakers, isolating switches, high voltage compressed air load breakers, high voltage isolating switches, etc.
It refers narrowly to low-voltage circuit breakers and more narrowly to molded case circuit breakers and small (miniature) circuit breakers.

Thus, it can be said that an air circuit breaker includes some circuit breakers, and circuit breakers are not necessarily all air circuit breakers (for example, SF circuit breakers).
It should be noted that leakage protection devices are an independent category of electrical appliances that differ from circuit breakers in that they are obsolete products that are currently recommended to be turned off. But some of our electricians often confuse them.
The leakage protection device only plays role of leakage protection, and must cooperate with circuit breaker to realize comprehensive protection of overload, short circuit and leakage. The leakage switch itself includes all of above functions.
Air circuit breaker and leakage protection selection principle
It is selected by wire size, not electrical power. The following configurations are for reference only and details depend on design of electrician.
1) Selecting main switch of air circuit breaker in household switch box. Generally, a 2P40~63A double-pole switch without leakage or with leakage is used (it is recommended to use a circuit breaker. During a thunderstorm, leakage protection of main switch may cause whole house to be unable to supply electricity, even lighting) . The main switch may be slightly larger and voltage will be very low during peak period of electricity consumption in summer, but shunt should not be large, otherwise it will not have a protective effect if it is too large.
2) The lighting circuit usually uses a small 10-16A air circuit breaker. For a wire size of 1.5mm², use switch C10; for a wire cross section of 2.5 mm² use switch C16/C20.
3) In a circuit with a common socket, a 16-20A leakage protection circuit breaker and a working current of 15-30mA are usually used. For wire cross section 2.5 mm² use switch C16/C20, for wire cross section 4 mm² use switch C25.
4) As a rule, 16-25 A miniature circuit breakers are selected for air conditioning circuit. In 1 hp air conditioners. and 1.5 hp 2.5 mm² wires are used, C16 and C20 switches are used respectively; in air conditioners with a capacity of 2 and 2.5 hp 4.0 mm² wires are used, respectively switches C25 and C32 are used; in cabinet air conditioners with a power of 3–5 hp. use 6.0mm² wire, use C40 switch, central air conditioner around 10P needs independent 2P40A.
5) It is best to use 6.0 mm² wire and C40 switch for electric water heater circuit. It is not recommended to use an instantaneous water heater with a power of about 7000 W, which will easily bring a great fire hazard into house.
6) For kitchen circuits andbathroom, it is recommended to use a switch of about 25A. Due to high humidity in kitchen and bathroom, it is advisable to use a leakage circuit breaker with a small operating current (such as 10~15mA) and a trip time of no more than 0.1s on corresponding branch.
Home branch circuit should be determined according to area of use and power consumption, and can generally be installed according to following rules:
1) 1~2 lighting circuits (2.5mm², open with C16). For residences with 3 bedrooms or less, one lighting circuit must be installed, and for residences with more than 3 bedrooms and an installed power supply capacity of more than 2kW, two lighting circuits must be installed.
2) One kitchen socket circuit (4 mm², with C25 leakage protection).
3) 1 bathroom electrical outlet (4 or 6 mm², use C25 or C32, C40 leakage protection). If both bathrooms are equipped with powerful electrical equipment, such as electric water heaters, then each bathroom must be equipped with an outlet. Bathroom lighting should be on same circuit as bathroom outlet. In absence of powerful electrical equipment in kitchen and bathroom in living room, electrical outlet in kitchen and bathroom and lighting in bathroom can be powered by a power circuit with an RCD.
4) In addition to kitchen and bathroom, other functional areas such as living room and bedroom should be equipped with 1-2 electrical outlets (2.5mm², C20 leakage proof) and number of outlets for each circuit is not must exceed 10 (groups).
5) 1 redundant circuit (for high power appliances, 4 or 6 mm², with circuit breaker).
Related
- What is difference between surge device, lightning arrester, leakage protection, circuit breaker and circuit breaker? Come and get knowledge
- Circuit Analysis of 6 Examples Explaining Lightning Surge Protection in Detail
- Power port lightning protection circuit
- What is difference between TVS tube and zener diode?
- What is difference between synchronous rectification and non-synchronous rectification?
- What is difference between thermocouple and RTD? Remember these points, do not choose wrong
- What is difference between 0 ohm resistors, inductors and magnetic balls for single point grounding?
- Is printed circuit board covered with copper very “up to mark”? One article to help you get practical guidelines and norms
- Optocoupler and application circuit
- What is difference between 0 ohm resistors, inductors and magnetic balls? After reading this I finally got the answer
Hot Posts
 How to distinguish induction from leakage, we will teach you three tricks! Ordinary people can also learn super practical
How to distinguish induction from leakage, we will teach you three tricks! Ordinary people can also learn super practical
- What is drowning in gold? Why Shen Jin?
- This is a metaphor for EMI/EMS/EMC that can be understood at a glance.
- How many types of pads have you seen in PCB design?
- Summary of Common PCB Repair Techniques
- What is three anti-paint? How to use it correctly?
- Knowing these rules, you will not get confused looking at circuit diagram.
- How to make anti-interference PCB design?
- Can diodes do this?