Location:Home Page > Archive Archive
Four leg inductor? Did you see it?
2023-04-11【Archive】
Our conventional inductors have two legs called differential inductors. Today I will introduce a common mode inductor with four legs.
Differential mode current and common mode current
Differential current: On a pair of differential signal lines, a pair of signals of same size and opposite direction is usually operating current in circuit. For a signal line, this is current flowing between signal line and signal ground line.
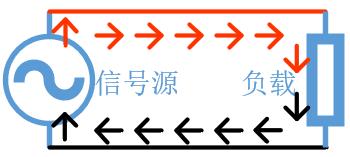
Common mode current: A pair of signals (or noise) with same magnitude and direction on a pair of differential signal lines. In a circuit, noise is usually carried to ground as common mode current, which is why it is also called common mode noise.
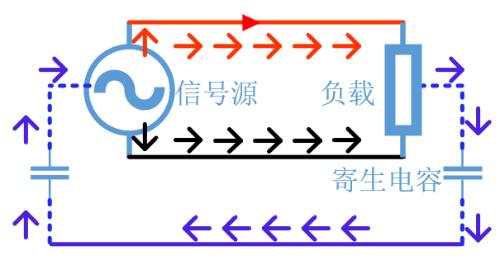
Common Mode Noise Rejection
There are many ways to suppress common mode noise. In addition to reducing common mode noise from source, usually most common method of suppression is to use common mode inductors to filter common mode noise, i.e., to block common mode noise outside target circuit. That is, common-mode choke devices are connected to line in series.
The purpose of this is to increase common-mode impedance so that common-mode current is drawn and blocked (reflected) by inductor, thereby suppressing common-mode noise on line.
The principle of a common mode choke or inductor
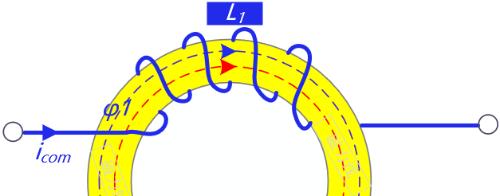
If a pair of coils are wound in same direction on a magnetic ring made of a certain magnetic material, when an alternating current passes through coil, a magnetic flux will be generated due to electromagnetic induction.
For differential mode signals, magnetic fluxes generated are of same magnitude and opposite directions, and they cancel each other out, so differential mode impedance generated by magnetic ring is very small.
For common-mode signals, magnitude and direction of generated magnetic flux are same and they overlap so that magnetic ring creates a large common-mode resistance.
With this feature, common mode inductor has less effect on differential signal, but provides good common mode noise filtering.
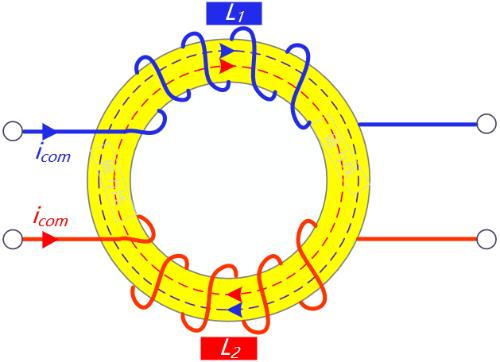
1) The differential current passes through common mode coil, direction of magnetic field line is opposite, and induced magnetic field is weakened. This can be seen from direction of magnetic field line in figure below. - solid arrow indicates direction of current, and dotted line indicates direction of magnetic field.
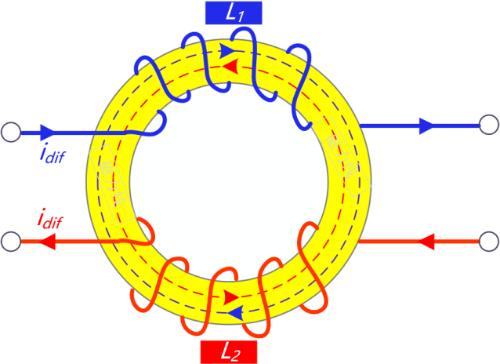
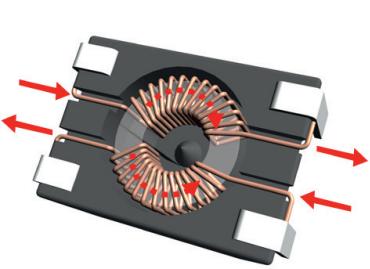
2) Common mode current flows through common mode coil, direction of magnetic field lines is same, and induced magnetic field increases. This can be seen from direction of magnetic field lines in figure below - solid arrow indicates direction of current, and dotted line indicates direction of magnetic field
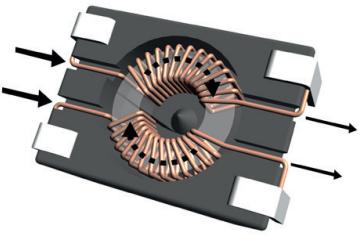
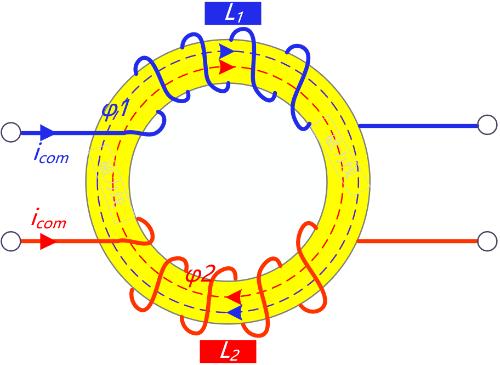
The inductance of a common mode coil is also known as self-inductance factor. We know that inductance is ability to characterize ability to generate a magnetic field.
For common mode coils or common mode inductors, when common mode current flows through coil, since direction of magnetic field lines is same, magnetic flux is superimposed without regard to leakage inductance, but principle of mutual inductance.
The magnetic force lines produced by red coil in figure below pass through blue coil, and magnetic force lines generated by blue coil also pass through red coil, inducing each other.
In terms of inductance, inductance is also multiplied, and flux linkage is total magnetic flux.
For common mode inductors, when magnetic flux is twice original, number of turns does not change and current does not change. At this time, inductance doubles compared to original, which means that equivalent magnetic permeability becomes 2 times greater than original.
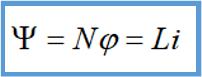
Why does equivalent magnetic permeability double? From following inductance formula, since number of turns N does not change, magnetic core and cross-sectional area of the magnetic core are determined by physical dimensions of magnetic core, so there is no change. The only thing is that magnetic permeability u doubles, so more can be generated magnetic flux.
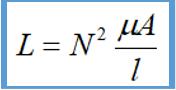
So, a common mode inductor operates in mutual inductance mode when a common mode current flows.
Under effect of mutual inductance, equivalent inductance is doubled, and common mode inductance is also doubled, so it has a good common-mode filtering effect, that is, common-mode signal is blocked. large impedance, Do not let it pass through common mode inductor, that is, do not let this signal be transmitted to next stage of circuit. The following is inductive reactance ZL produced by inductor.
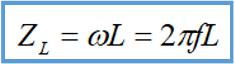
To understand inductance of common mode inductors in common mode, main thing is to understand mutual inductance and all magnetic components. No matter what it's called, as long as you understand changing shape of magnetic field and see essence of changing magnetic field through this phenomenon, it will be easy for you to understand it.
In addition, we must always understand lines of magnetic field, which are intuitive shapes for us to understand magnetic field. Just imagine that regardless of concepts or phenomena of magnetic field, such as end of same name or opposite end, or mutual inductance, we all draw lines of magnetic force in order to understand them - explain before mastering "magnet rod winding method".
Related
- Four leg inductor? Did you see it?
- Four Magic DMM Methods You Should Know
- Did you pay attention to details of using relay?
- Do you know four magical ways to use a digital multimeter?
- A list of most common PCB design mistakes, see how many mistakes have you made?
- You can't think about it, can you? A small resistor can be great too
- Does PCB use copper mesh or solid copper, are you using it correctly?
- Why did your 4.7uF capacitor become 0.33uF? too weird
- Four Tricks to Make Your Boost Circuit Safer
- How did BUCK scheme come about? Application: 3 kinds of evolutionary chains
Hot Posts
 How to distinguish induction from leakage, we will teach you three tricks! Ordinary people can also learn super practical
How to distinguish induction from leakage, we will teach you three tricks! Ordinary people can also learn super practical
- What is drowning in gold? Why Shen Jin?
- This is a metaphor for EMI/EMS/EMC that can be understood at a glance.
- How many types of pads have you seen in PCB design?
- Summary of Common PCB Repair Techniques
- What is three anti-paint? How to use it correctly?
- Knowing these rules, you will not get confused looking at circuit diagram.
- How to make anti-interference PCB design?
- Can diodes do this?