Location:Home Page > Archive Archive
A simple understanding of op amps...
2023-03-18【Archive】
The invention of operational amplifier has a long history. From earliest vacuum tube to today's integrated circuit, it has always played a key role in various electronic products. And advent of new applications such as information devices, mobile phones, PDAs and networks has taken op amps to next level.
01 A brief introduction to operational amplifier
An op amp (abbreviated as op amp) is a very high gain circuit. In real circuits, some functional module is usually combined with a feedback circuit. This is an amplifier with a special coupling circuit and feedback. Its output can be result of mathematical operations such as addition, subtraction, or differentiation and integration of input signal.

Because in early days it was used in analog computers to perform mathematical operations, it was called an "op-amp". An operational amplifier is a functionally named circuit device that can be implemented as a discrete device or a semiconductor chip. With development of semiconductor technology, most operational amplifiers exist in form of a single microcircuit. There are many types of operational amplifiers that are widely used in the electronics industry.
OpAmp Development History 02
1941
1941: Carl D. Schwarzel, Jr. of Bell Laboratories invented first vacuum tube op amp and received U.S. Patent 2,401,779 titled "Summing Amplifier";
1952
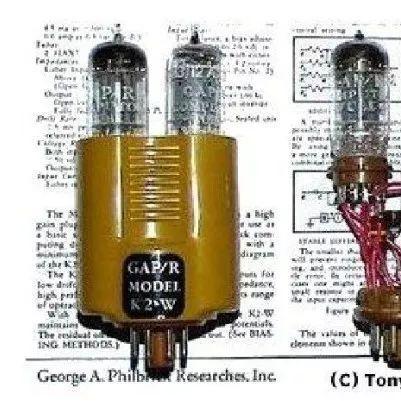

1952 The first commercial product sold as a commercial product was a tube op amp from George A. Philbrick Researches (GAP/R), model K2-W;
1963
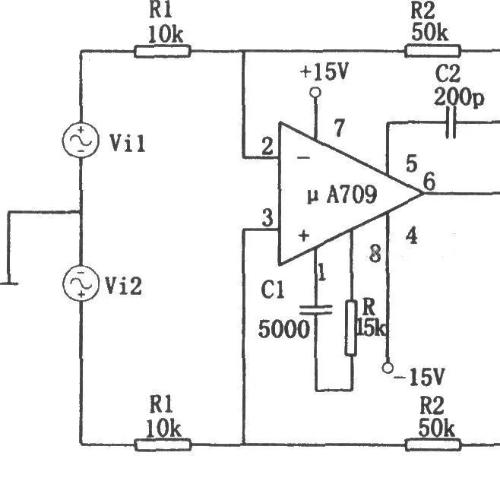
1963: The first single integrated circuit op amp was µA702 designed by Bob Widlar of Fairchild Semiconductors, and µA709 was released in 1965 after modification;
1968

1968: Fairchild Semiconductor introduces µA741. It is still used in production to this day, it is most successful op-amp of all time and one of very few IC models with longest lifespan.
03 Basic knowledge of operational amplifiers
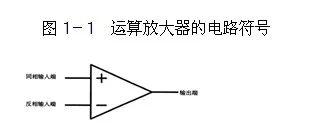
The op amp has two input terminals and one output terminal, as shown in figure below, input terminal marked with "+" is "non-inverting input terminal" and cannot be called positive terminal), and other marked with "one" . The sign input terminal "is inverting input terminal" and cannot be called a negative terminal. If same signal is supplied from these two input terminals in series, an output signal with same voltage but opposite polarity will be obtained at output terminal: output The output signal at terminal is in phase with signal at non-inverting input terminal and is inverted with signal at inverting input terminal. input terminal.
The power supply connected to op-amp can be single or dual, as shown in the figure below.

Op-amps have some very interesting characteristics that can be used flexibly for many unique purposes. In general, these characteristics can be combined into two:
1. The increase of operational amplifier is infinite.
2. The input impedance of an op amp is infinite and output impedance is zero.
Now let's take a quick look at what conclusions can be drawn from above two properties.
First, gain of an op-amp is infinite, so as long as input voltage of its input terminal is non-zero, output terminal will have an output voltage equal to positive or negative power supply. output voltage must be infinitely high, but limited by supply voltage. To be precise, if input voltage to non-inverting input is higher than input voltage to inverting input, even if it is only slightly higher, output of op-amp will produce a voltage that is same as positive. supply voltage; If input voltage at common-mode input is higher than input voltage at non-inverting input, output of op-amp will be an output voltage equal to negative supply voltage (if op-amp uses a single supply, output voltage will be zero).
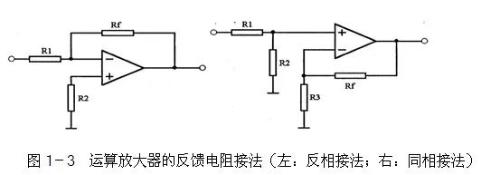
Second, because gain is infinite, op amp cannot be used directly as an amplifier, and output must be fed back to an inverting input (called negative feedback) to reduce its gain. As shown in left diagram of Figure 1-3, function of resistor R1 is to return output signal to inverting input of op amp. Since voltage at inverting input is opposite to output voltage, gain of circuit will decrease. , is a negative feedback circuit, and resistor Rf is also called a negative feedback resistor.
Also, since input of op-amp is infinite, no current is applied to input of op-amp - it only accepts voltage. Similarly, if you imagine that there is an infinite resistor between non-inverting input and inverting input of op-amp, then voltage applied across resistor cannot produce current. two input terminals of op amp are same (the voltage in this case is a bit like shorting two input terminals with a wire, so we call this phenomenon "Not short enough").
Related
- A simple understanding of op amps...
- If you don't know characteristics of these 5 power amps, you are wrong...
- Deep Understanding of Analog Electronics - Analog Electronics Tutorial
- 11 classic op amp circuits
- Finally, it becomes clear that process of obtaining switching losses of a MOSFET in a switching power supply
- Analysis of power circuit of a classic single-chip microcomputer
- Analysis of damping RC circuit of a switching power supply "haberdashery"
- Understanding input impedance and output impedance
- Detailed analysis of the "various protection schemes" of a switching power supply
- A list of some of the tools commonly used by electronic engineers.
Hot Posts
 How to distinguish induction from leakage, we will teach you three tricks! Ordinary people can also learn super practical
How to distinguish induction from leakage, we will teach you three tricks! Ordinary people can also learn super practical
- What is drowning in gold? Why Shen Jin?
- This is a metaphor for EMI/EMS/EMC that can be understood at a glance.
- How many types of pads have you seen in PCB design?
- Summary of Common PCB Repair Techniques
- What is three anti-paint? How to use it correctly?
- Knowing these rules, you will not get confused looking at circuit diagram.
- How to make anti-interference PCB design?
- Can diodes do this?