Location:Home Page > Archive Archive
The most complete knowledge in history of uninterruptible power supply UPS
2023-04-05【Archive】
UPS is an uninterruptible power supply. It is usually one of engineering subsystems of computer room of weak power grid, which connects battery with main equipment, and is mainly used to ensure stable and uninterrupted power supply to equipment.

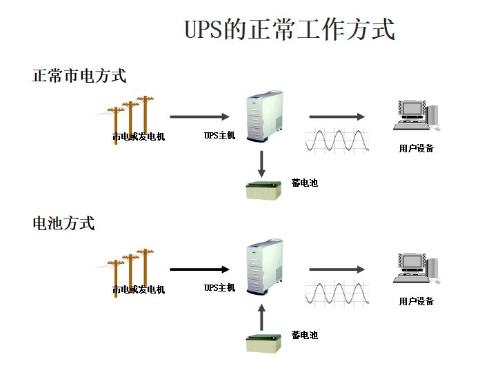
When mains input is normal, UPS stabilizes mains and supplies it to load. At this time, UPS acts as an AC voltage stabilizer and also charges battery inside machine; when mains power is off (In event of a power outage due to an accident), UPS immediately transfers DC power of battery to load through inverter switching method to continue to supply AC 220V power, so that load can maintain normal operation and protect software and hardware download from damage.
UPS devices typically provide overvoltage or undervoltage protection. Let's take a look at basics of UPS.
01 UPS basic principle
What is a UPS?
Use battery chemical energy as backup energy, a power conversion device that continuously provides electrical power (AC) to user equipment in event of network failures such as power outages.
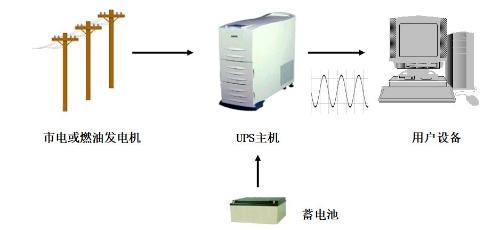
Why do you need a UPS?
Power supply from mains looks normal, but it is unreliable: normal surface power is actually dangerous.
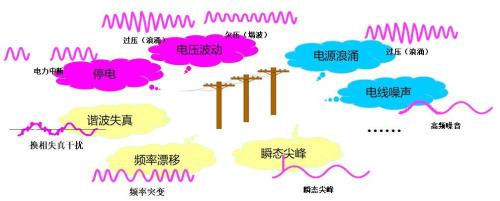
Power outage
Data loss, communication interruption, business opportunity delay...
—— direct losses estimated at RMB 5,000-100,000 per minute
Equipment failure, instrument failure, work interruption...
— Indirect economic losses are immeasurable
Food pollution
Short-term power surges, surges, high voltage surges
Causing hardware damage to servers, routers, disk arrays, etc.
Harmonic pollution, inter-line noise and frequency drift
The bit error rate of network transmission is greatly increased and data rate is low
The four main functions of a UPS
No power off function - to solve problem of power off
AC voltage stabilization function - can solve problem of large fluctuations in mains voltage
Cleaning function - to solve problem of pollution of network and electricity
Control Function - Solving AC Service Problems
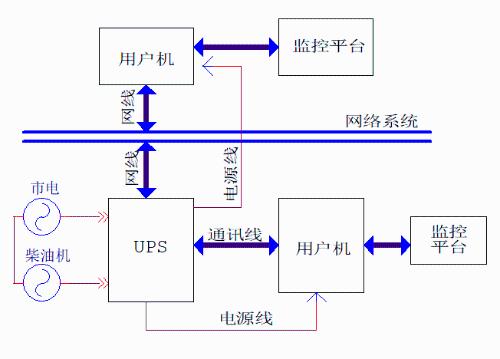
UPS system structure
The monitoring platform is also one of most important components of UPS
Main technical parameters of UPS 02
Enter attributes:
1. Input Voltage Range A wide input voltage range reduces chance of battery drain and prolongs battery life.
2.Input power factor The power factor is low, input reactive power is large, and harmonic current pollutes power system, affecting other equipment and causing interference.
3. Permissible mains frequency range.
4. Harmonic components of input current. (PFC, 6/12 pulse transformer)
Output properties:
1. Static stability. 1% for large and 2% for small and medium.
2. Output transient characteristics. Large 5%, small and medium 8%.
3. output overload capacity. (for example: overload 125% for 5 minutes; 150% for 10 seconds)
4. Output power factor. (0.8, 0.9, 1)
5. Harmonic distortion of output voltage. Typically within 3%.
03 UPS configuration and calculation
The UPS system mainly consists of following parts:
UPS Host
Required features (e.g. BCB BOX etc.)
Battery
Support battery cabinet/rack, battery switch, etc.
Function options (e.g. lightning protection, monitoring, harmonic control, outgoing line, etc.)
Calculation required:
Calculation and selection of capacity of UPS node
Capacity calculation and UPS backup battery selection
04 UPS power calculation and selection
First get total power consumption of load and unify unit to kVA.
For example: a normal PC load is about 200 VA, a small server load is about 1500 VA, and a large and medium server load is about 3000 VA.
Conversion ratio between current I (amps) and power consumption W (watts) and VA:
BA= I*220
VA=W/0.8 (generally considered 0.7 below 20kVA and 0.8 above 20kVA)
Given that UPS is operating in 60% to 80% range, which is best operating condition, it is generally recommended to divide above result by 0.8 and scale up again in calculation.
Then select nearest power product in product manual and use constant power mode calculation method
W/cell = PL/(N×6×η)
05 UP Power Supply Diagram Introduction
Centralized power supply:
Advantage: It can realize equipotential control of network equipment resources and reduce transmission error rate.
Disadvantages. The initial investment is great, and consequences of a single machine failure are great.
Decentralized food method:
Benefits: Flexible circuit layout, less impact of failure.
Disadvantages: If entire device cannot be placed on same ground line, it can easily cause interference.
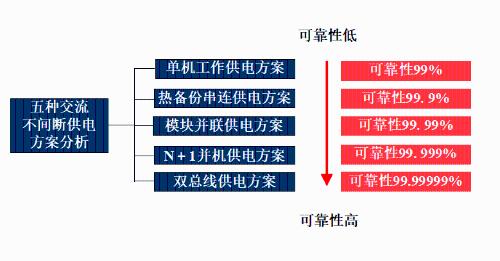
Single machine power supply:
The easiest UPS solution
The capacity of AC power system at each scattered location is generally below 6 kVA
Each AC load point is independently powered by UPS
Electricity is usually supplied from nearest outlet
Hot Standby Master-Slave Series:
Suitable for small to medium sized networks, server farms, offices, tools, etc.
Consists of master UPS, slave UPS, battery system, power distribution system
Simple power distribution design and engineering
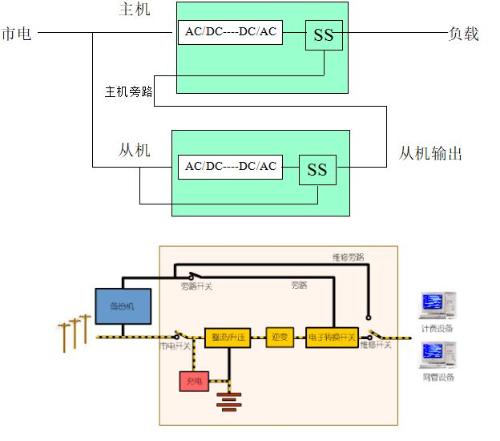
Benefits:
1. Two or more UPSs are generally in a relatively independent and non-interfering operating state.
2. The performance requirements for synchronous UPS monitoring are relatively low.
3. Use different UPS models and capacities for daisy-chained hot standby.
Weaknesses:
1. The driven machine is idling for a long time and its efficiency is low.
2. The battery is in a state of floating charge for a long time, and there is little opportunity for regular maintenance when discharging under load, which will affect life of battery.
3. The wingman must have good lifting capacity in increments.
4. Long-term operation, main inverter = good static bypass conversion function is key
No extension function.
5. Compared to a "parallel" redundant system, mean time between failures is relatively short.
Module parallel power supply:
All AC loads are centrally powered by a modular parallel UPS
Modular UPS includes: Racks, Parallel Power Modules, Parallel Battery Modules, Charging Modules, etc.
Suitable for small to medium sized networks, server farms, offices, tools, etc.
Consists of rack, UPS power module, battery module, power distribution system
The power module is configured for N+1 redundancy, which reduces mean downtime.
General input, output, parallel battery system, control system
N+1 Direct Parallel Redundancy
Suitable for medium to large networks, data centers, building district power, industrial plants and mines, etc.
It consists of N+1 directly parallel UPS, battery modules and power distribution systems.
The system has N+1 redundancy, and its reliability is higher than that of a standalone UPS.
Easy to expand and maintain.
The most widely used schema.
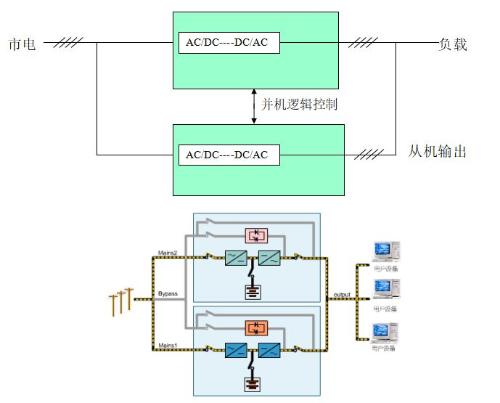
Benefits:
1. The advanced phase-locked synchronization technology ensures even distribution of load current when multiple UPSs are connected in direct parallel.
2. Good expansion performance (N+1).
3. Avoid disadvantages of "sequential" hot backups.
Weaknesses:
1. It places high demands on genlock technology of device itself.
2.High requirements for equipment manufacturing technology - output impedance is close.
3. High requirements for characteristics of regulation of output voltage of inverter - phase regulation.
4. The UPS must be same model and capacity.
5. When multiple devices are connected in parallel, bypass must also increase "current inductance".
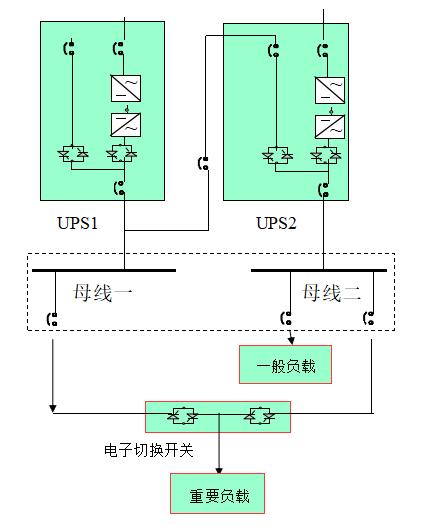
Double bus:
Solve single-point bottleneck in single-bus mode. Further increase of system reliability. The system configuration is complex, investment is large, and installation and debugging requirements are high.
Related
- The most complete knowledge in history of uninterruptible power supply UPS
- Super practical! The 10 Most Commonly Used Power Supply Design Formulas
- Engineer Daniel tells you: The "Y Capacitor" of a switching power supply is calculated in this way.
- Analysis and comparison of 6 most commonly used DC power supply circuits
- Detailed analysis of the "various protection schemes" of a switching power supply
- Four ways to reduce the output "ripple and noise" of a switching power supply
- The most complete test of iron 5 processes, one less will not work
- Finally, it becomes clear that process of obtaining switching losses of a MOSFET in a switching power supply
- Analysis of damping RC circuit of a switching power supply "haberdashery"
- Do not underestimate "form of high-frequency magnetic core" in switching power supply, what effect does it have on transformer?
Hot Posts
 How to distinguish induction from leakage, we will teach you three tricks! Ordinary people can also learn super practical
How to distinguish induction from leakage, we will teach you three tricks! Ordinary people can also learn super practical
- What is drowning in gold? Why Shen Jin?
- This is a metaphor for EMI/EMS/EMC that can be understood at a glance.
- How many types of pads have you seen in PCB design?
- Summary of Common PCB Repair Techniques
- What is three anti-paint? How to use it correctly?
- Knowing these rules, you will not get confused looking at circuit diagram.
- How to make anti-interference PCB design?
- Can diodes do this?