Location:Home Page > Archive Archive
What is nature of GND ground wire in a circuit?
2023-08-16【Archive】
Ask a simple but complex circuit question: What is nature of GND wire in a circuit?
In process of routing a PCB, engineers will encounter different GND handling.

Why is this? During circuit design phase, in order to reduce mutual interference between circuits, engineers usually introduce different GND wires as 0V reference points for different functional circuits to form different current loops.
GND ground classification
1. Analog ground AGND
Analog ground wire AGND is mainly used in analog circuit part, such as analog sensor ADC data acquisition circuit, working gain circuit, etc. In these analog circuits, since signal is an analog signal and is a weak signal, to it easily affected by large current of other circuits. If no distinction is made, high current will cause a large voltage drop in analog circuit, which will distort analog signal and can seriously disrupt operation of analog circuit.
2. DGND Digital Ground
DGND digital ground wire, obviously compared with AGND analog ground wire, is mainly used for digital circuit parts, such as key detection circuit, USB communication circuit, single-chip microcomputer circuit and so on. The reason why DGND digital ground wire is installed is because digital circuits have a common characteristic, which is a discrete switching signal, only number "0" and number "1" differ, as shown in figure . in picture below.
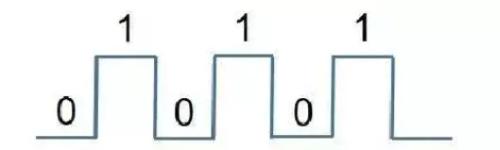
During transition from digital voltage "0" to digital voltage "1" or from digital voltage "1" to digital voltage "0", voltage changes according to Maxwell electromagnetic field. Theoretically, a magnetic field will be created around changing current, which will form electromagnetic radiation for other circuits.
Under no circumstances should a separate DGND digital ground wire be used to effectively isolate other circuits in order to reduce effects of electromagnetic radiation from a circuit.
3. Power ground wire PGND
Whether analog ground wire AGND or digital ground wire DGND, they are all low power circuits. Large power circuits such as motor drive circuits, solenoid valve drive circuits, etc. also have a separate reference ground called PGND power ground.
High power circuits, as name suggests, are relatively high current circuits. Apparently, large currents can easily cause ground shifts between different functional circuits, as shown in figure below.
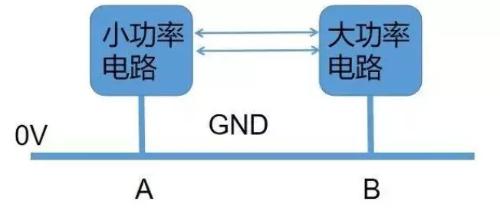
Because there is a ground bias in circuit, original 5V voltage may not be 5V, but become 4V. Since 5V voltage refers to GND 0V ground wire, if ground bias increases voltage of GND ground wire from 0V to 1 V, then previous voltage 5V (5V-0V=5V) becomes current 4V (5V-1V=4V). too much.
4. Ground GND
Analog ground wire AGND, digital ground wire DGND and power ground wire PGND are classified as DC ground wire GND. These different types of ground wires are eventually combined into a 0V reference ground wire. This ground wire is called GND power ground wire.
The power supply is source of energy for all circuits. The voltage and current required to operate all circuits are supplied by power supply. Therefore, ground wire GND of power supply is 0 V reference point for all circuits.
Therefore, other types of ground, whether analog ground AGND, digital ground DGND or power ground PGND, must be connected to power ground GND at end.
5. AC ground wire CGND
The CGND AC ground wire is typically present in circuit elements containing AC power, such as AC to DC power circuits.
AC-DC power supply circuit divided into two parts. The front stage in circuit is AC part and back stage in circuit is DC part, resulting in two ground wires: one is AC ground wire and other is DC ground wire.
The AC ground wire is used as 0 V test point of AC part, and DC ground wire is used as 0 V test point of DC part. Typically, to combine GND ground wire in circuits, engineers connect AC ground wire to DC ground wire through a decoupling capacitor or inductor.
6. EGND
The safety voltage of human body is below 36V. If a voltage greater than 36V is applied to human body, it will cause damage to human body. This is common sense for engineers when developing and designing circuit solutions. .
In order to improve circuit's safety factor, engineers commonly use ground wire EGND ground in high voltage and high current projects such as household appliance electric fans, refrigerators, televisions and other circuits. Socket with protective earth conductor EGND, as shown in the figure below.

Why 3 pins for a household appliance socket? For 220 V AC, you only need a live wire and a neutral wire, two are enough, so why are there 3 terminals in socket?
The socket has three terminals, two of which are used for 220V live wire and neutral wire, and other terminal is EGND ground wire for protection.
The chip brother should indicate that EGND ground wire is connected to our earth only for high voltage protection, it does not participate in project circuit function and has nothing to do with circuit function. .
Therefore, EGND ground wire has an obvious pattern, meaning it is different from other types of GND ground wire.
More about GND principle
Engineers may ask, how can there be so many differences in GND ground wire, and how can a simple circuit problem be so complex?
Why do we need to introduce so many separate GND functions?
For this kind of ground wire design problem, GND is usually referred to by engineers as simply GND, which is indistinguishable during circuit design process, making it difficult to effectively identify GND of various circuit functions during PCB wiring. Grounding, directly and simply connect all GNDs together.
While this is easy to do, it will cause a number of problems:
1. Signal crosstalk
If GND ground wires with different functions are directly connected to each other, a high power circuit passing through GND ground wire will affect 0 V GND reference point of low power circuit, creating crosstalk between signals of different circuits.
2. Signal Accuracy
Analog circuit, main indicator of its evaluation is accuracy of signal. Without precision, analog circuit loses its original functional meaning.
Because CGND ground wire of an AC power supply is a sine wave, it periodically oscillates up and down, and its voltage also fluctuates up and down, instead of always maintaining a constant 0V like a DC ground wire GND. .
Connect GND wires of different circuits together, periodically changing AC ground wire CGND will cause analog circuit ground wire AGND to change, which will affect accuracy of analog signal voltage.
3. EMC experiment
The weaker signal, weaker EMC of external electromagnetic radiation; stronger signal, stronger EMC of external electromagnetic radiation.
If GND wires of different circuits are connected together, GND ground wire of strong signal circuit will directly interact with GND wire of weak signal circuit. The consequence of this is that EMC electromagnetic radiation, which was originally a weak signal, has also become a signal source with strong external electromagnetic radiation, which complicates processing of EMC experiment scheme.
4. Schema Reliability
The smaller signal coupling between systems of a circuit, greater ability of circuit to operate independently; greater signal coupling, weaker circuit's ability to operate independently.
Just imagine, if there is no intersection between two circuits A and circuits B, function of circuits A obviously cannot affect normal operation of circuits B, and function of circuits B is also good. or bad. It also cannot affect normal operation of circuit A system.
It's like a couple of strange men and women. Before they become lovers, girl's emotional changes will not affect boy's mood, because they have no intersection.
If in a chain earthing system circuits with different functions are connected together, this is tantamount to an increase in interference link between circuits, that is, a decrease in reliability of circuit.
Related
- What is nature of GND ground wire in a circuit?
- What is a delay scheme? Explanation of 6 Kinds of Delay Circuit Principles
- Principal analysis of BUCK / BOOST circuit, a summary is also in place
- What is purpose of connecting a polar capacitor and a non-polar capacitor in parallel?
- In circuit design, what are differences between six types of grounds?
- What does inside of a multilayer PCB look like? Three-dimensional general analysis of design process of high-quality printed circuit boards
- Experience in recognition of circuit diagrams of electronic circuits and method of circuit analysis
- Explain in detail difference and application of two-three-four-wire system.
- Analysis of power circuit of a classic single-chip microcomputer
- Analysis of damping RC circuit of a switching power supply "haberdashery"
Hot Posts
 How to distinguish induction from leakage, we will teach you three tricks! Ordinary people can also learn super practical
How to distinguish induction from leakage, we will teach you three tricks! Ordinary people can also learn super practical
- What is drowning in gold? Why Shen Jin?
- This is a metaphor for EMI/EMS/EMC that can be understood at a glance.
- How many types of pads have you seen in PCB design?
- Summary of Common PCB Repair Techniques
- What is three anti-paint? How to use it correctly?
- Knowing these rules, you will not get confused looking at circuit diagram.
- How to make anti-interference PCB design?
- Can diodes do this?